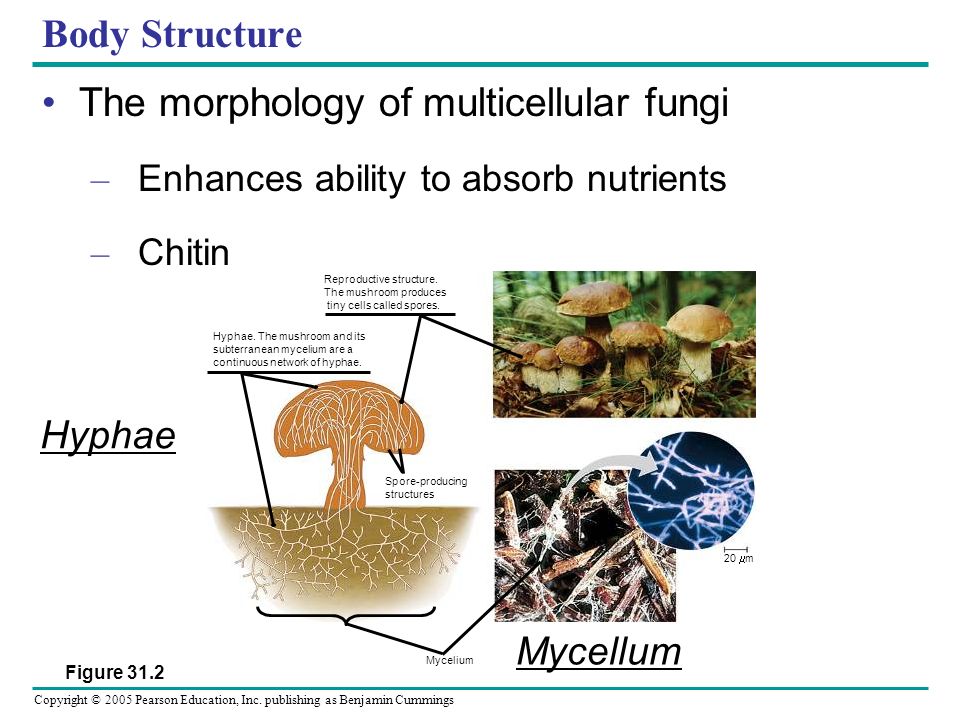
Structure Of Multicellular Fungi Masteringbiology - Body Structure The morphology of multicellular fungi Enhances ability to absorb nutrients Chitin Hyphae. Were always here.
Https Webcourses Ucf Edu Files 77478335 Download Download Frd 1
Most of the fungi are filamentous and the vegetative assimilative stage is a tubular branching thread-like filament called a hypha plural hyphae.
Structure of multicellular fungi masteringbiology. Some fungi are pathogens for example the fungal infection which causes athletes foot. The rest of the life cycle is characterized by the growth of mycelia. This fruiting body known as the sporocarp is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures form.
The structure of fungi can be explained in the following points. Any polysaccharide that is a polymer of glucose. Morphology of Fungi 1.
Have cell walls made of chitin 3. It is a bread mold that also causes blight in rice seedlings. Fungi are a monophyletic group and all fungi share certain key characteristics.
An example of a multicellular fungus is Rhizopus stolonifera. Several mycelia grouped together are a mycelium and these structures form the thallus or body of the mold. Join our Discord to connect with other students 247 any time night or day.
It consists of filaments called hyphae that can bunch together into structures called mycelia. These hyphae together form a mesh-like structure. By systematically analyzing 72 complete genomes we here show that hyphae evolved early in fungal evolution probably via diverse genetic changes i.
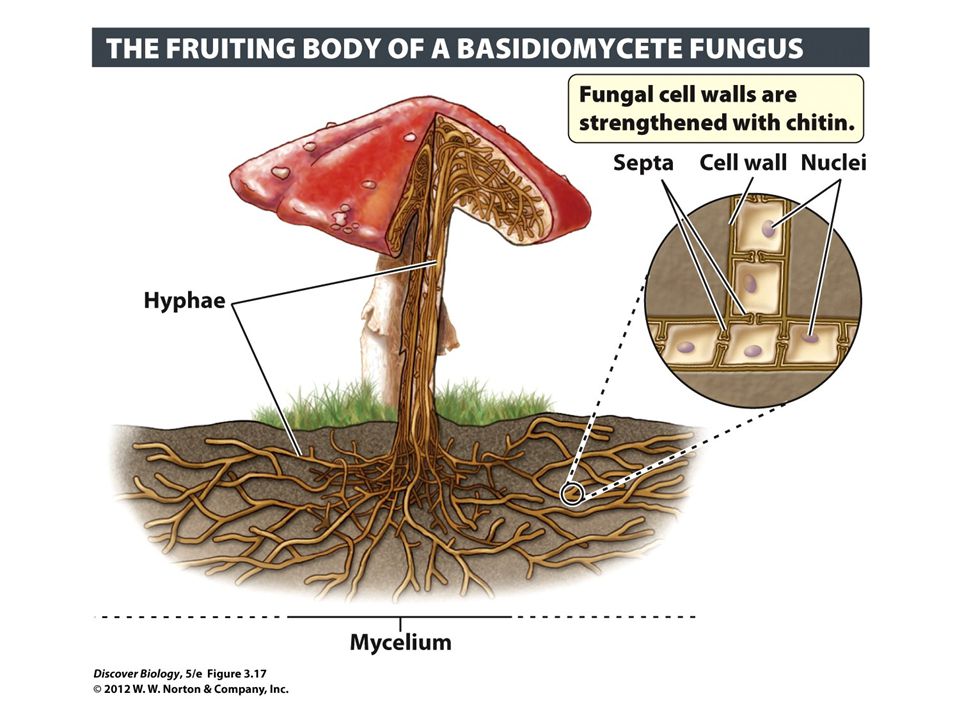
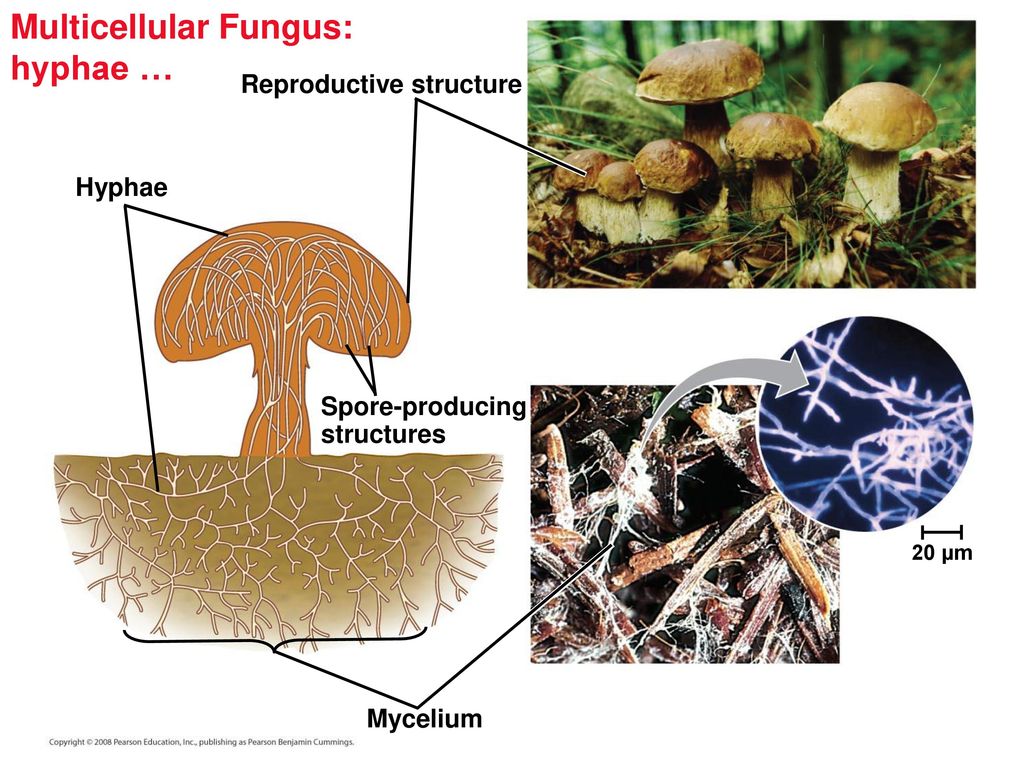
Spore-producing structures 20 µm Mycelium. The mushroom produces tiny cells called spores. Hyphae represent a hallmark structure of multicellular fungi.
Hyphae can form a tangled network called a mycelium and form the thallus body of fleshy fungi. The mushroom and its subterranean mycelium are a continuous network of hyphae. The fruiting body is part of the sexual phase of a fungal life cycle.
Fungi consist of long thread-like structures known as hyphae. Heterotrophs - digest food with secreted enzymes exoenzymes external digestion 2. Hyphae represent a hallmark structure of multicellular fungi.
Mold is a multicellular fungus. The molds for example are a large group of microscopic fungi that include many of the economically important plant parasites allergenic species and opportunistic pathogens of humans and other animals. The functional equivalent of cholesterol found in cell membranes of fungi and some protists as well as the steroid precursor of vitamin D2.
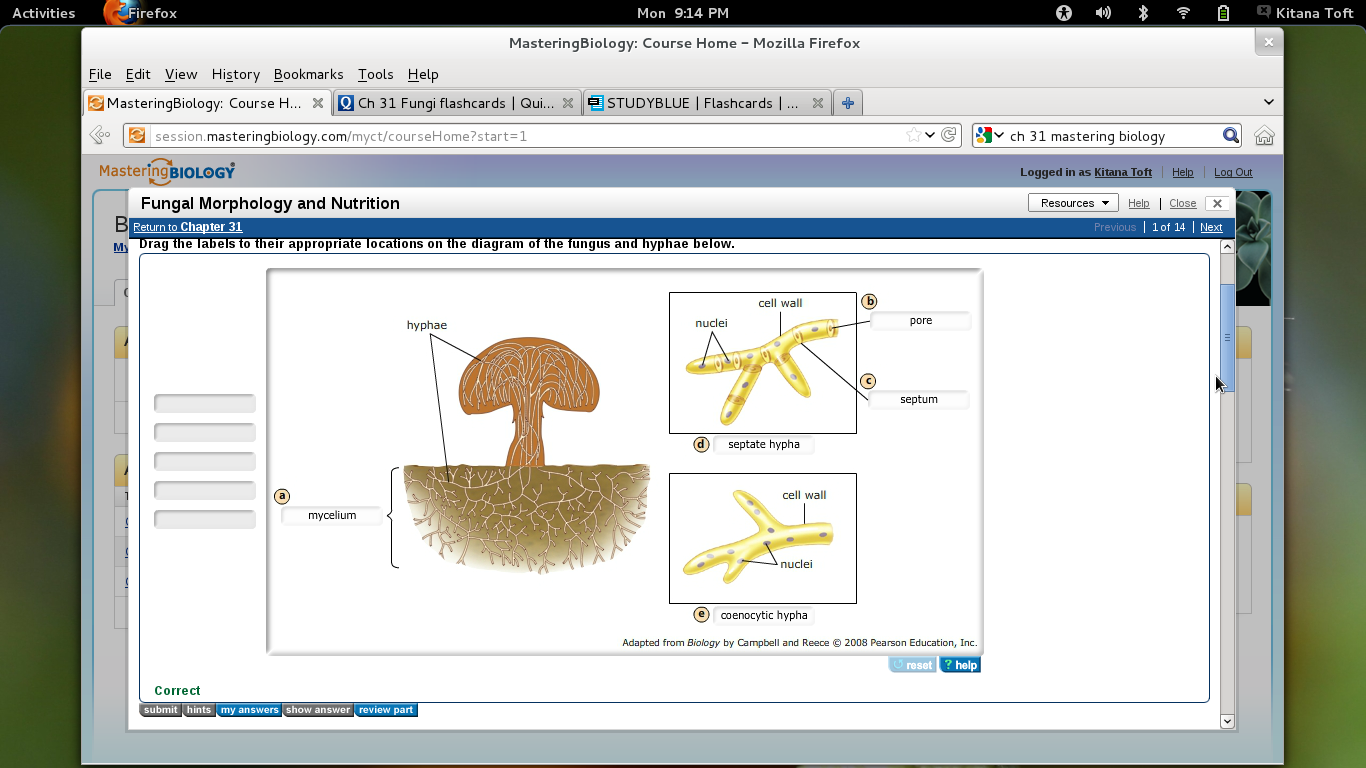
Hyphae that have walls between the cells are called septate hyphae. Almost all the fungi have a filamentous structure except the yeast cells. Most are multicellular with slender filamentous units called hyphae Label the diagram below Use Textbook figure 313.
Classification of fungi morphology and structure Pathogenicity Diagnosis Useful Properties of Fungi Diverse group of chemo heterotrophs Over 100000 fungal species identified Only about 100 are human or animal pathogens Saprophytes Digest dead organic matter. Macroscopic fungi such as morels mushrooms puffballs and the cultivated agarics available in grocery stores represent only a small fraction of the diversity in the kingdom Fungi. Multicellular fungi reproduce by making spores.
The vegetative body of a fungus is called a thallus and can be unicellular or multicellular. Some fungi take on different shapes depending on their environmental conditions. Most multicellular fungal bodies commonly called molds are made up of filaments called hyphae.
A long branching filamentous structure of a. They can be either single-celled or multicellular organism. Multicellular Filamentous with hyphae Produce conidia.
Describe the general structure of multicellular fungi. The feeding structure of a multicellular fungus is the mycelium which consists of numerous small-diameter filaments or hyphae. The evolutionary origins of hyphae and of the underlying genes are however hardly known.
Some fungi are dimorphic because they can go from being unicellular to multicellular depending on environmental conditions. The hypha extends by tip growth and multiplies by branching creating a fine network called a mycelium. Compared to other eukaryotes the special development of the tubular hyphae gives however the multicellular fungi a distinctive position because of their multinuclear coenocytic or septate structures Mouriño-Pétez 2013 which provide a continuous cytoplasm and ease cytosolic streaming and because of their interconnected hyphal networking abilities which helps to not face group conflicts between individual cells.
Unicellular fungi are generally referred to as yeasts. The vegetative part of any fungus consisting of a mass of branching threadlike hyphae often underground. Fungal structure A multicellular fungus showing rounded spore cases and spores and thread-like hyphae.
Hyphae that lack walls and cell membranes between the cells are called nonseptate. The evolutionary origins of hyphae and of the underlying genes are however hardly known. Nutrients absorbed by the hyphae can flow throughout the mycelium in both coenocytic hyphae and septate hyphae.
Bif 26 The Colonization Of Land By Plants And Fungi Ppt Download
Http Www Inetteacher Com Upload1 105022 Docs Biology 1021 Unit 1 Notes Pdf
Discover Biology Fifth Edition Ppt Download
Chapter 17 The Evolution Of Plant And Fungal Diversity Ppt Download
Get Answer Drag The Labels To Their Appropriate Locations On The Diagram Transtutors
Pearson Homework Questions Chapters 27 31 Flashcards Quizlet
Homework 10 Ch 31 Fungi Flashcards Quizlet
Bio 101 Ch 30 Flashcards Quizlet
Multicellular Fungus Hyphae Ppt Download
Copyright C 2005 Pearson Education Inc Publishing As Benjamin Cummings Body Structure The Morphology Of Multicellular Fungi Enhances Ability To Absorb Ppt Download
Vector Illustration Structure Multicellular Fungi Colourful Stock Vector Royalty Free 1015943803
Ch 31 Fungi Flashcards Chegg Com
Chapter 31 Biology Homework And Readings Flashcards Quizlet
Chapter 31 Mastering Biology Flashcards Quizlet